Do you know how Cubic Capacity can affect your shipments?
Almost every carrier we utilize through our LTL platforms has a cubic capacity rule in their rules tariff that may affect any of your shipments. LTL carriers impose minimum cubic capacity rules to effectively counter very light, fluffy shipments that take up more than their fair share of a trailer. In most cases, LTL carriers state that if a shipment consumes 750 cubic ft. of space or more, AND the shipment has a density of less than 6 pounds per cubic foot (pcf), it’s not paying its fair share. While the rule varies dramatically amongst carriers, most artificially adjust the weight to a minimum of 6 pcf, AND apply a class of 125 or 150 to the commodities being shipped with their associated tariff rates. Most carriers use the 750 cubic feet as the threshold, but not all.
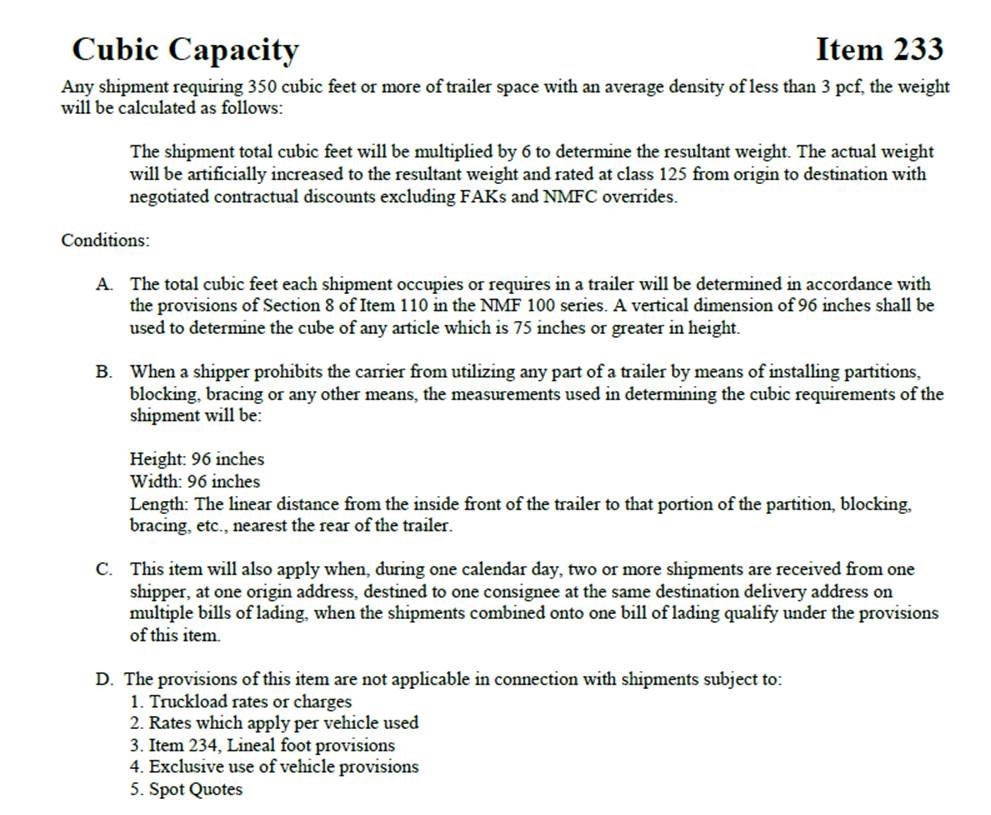
This week we wanted to clarify what to watch for with Cubic Capacity by providing an example from XPO:
XPO is now enforcing their standard cubic capacity rules on all tariffs. What this means is that shipments requiring 350 cubic ft. or more of the trailer with an average density of less than 3 pcf will have the weight calculated differently then what the actual weight is. Yes that is correct, the actual weight will not matter!
350 cubic ft. of the trailer equates to approximately 5.46 linear ft. of the trailer so you can see that we are severely limited on the amount of skids of LTL we can ship when the density is below 3 pcf.
As an example, for two pallets of LTL, cubic capacity would be calculated as follows. Please note that the carrier uses the actual height (96”) of the trailer when they look at the cubic capacity of the shipment, not the actual height that the shipment might be:
One skid = (40” x 43” x 96”) / 1726 cubic inches per cubic ft. = 95.67 cubic ft. x two skids = 193.34 cubic ft.
You can see that this falls way under the 350 cubic ft. rule so we are safe to ship this with XPO.
However, if you want to ship 4 skids, the cube of the shipment is now double at 386.68 cubic ft. which is outside of the cubic capacity limit. The only way you could ship this as an LTL shipment is if the density of the shipment was greater than 3 pcf.
Four skids with a total weight of 500 lbs., the density would be the 500 lbs. / 386.68 cubic ft. = 1.3 pcf.
If we shipped this LTL, we would be hit with the cubic capacity rule and our cost would skyrocket.
Four skids would have to have a total weight of 1161 lbs. or greater for us to be able to ship them as a standard LTL shipment with no problems. 1161 lbs./386.68 = 3.0 pcf.
Below is the actual excerpt from the XPO rules tariff: